Self-Employed vs. Small Business Owner: Why the Difference Matters
The differences between the self-employed and small business owners may appear subtle, but they can impact your expenses, liability, and taxes. Being a small business owner comes with additional challenges and responsibilities that self-employed individuals do not have. In this article, we define what it means to be self-employed and a small business owner, highlight the pros and cons of each, and explore two key differences.
Related posts:
- Owner's draw vs. Salary
- Need Help Funding Your Business? Here Are Your Options
- W2 Employee vs 1099: Which is Better For Your Business Needs?
What Does It Mean to Be Self-Employed?
If you’re self-employed, you work for yourself, and by yourself. You're the business. Your income depends on your own efforts, and you’re responsible for all aspects of your work.
Common self-employed structures:
- Sole proprietorship: A sole proprietor is in essence, a one-person business. You are the business; there is no distinction made between you and your business for tax and legal purposes. You are considered the same legal entity. Sole props. can operate by their given name (John Smith) or use a fictitious name (John's Carpet Cleaning), known as a DBA.
- Partnership: A partnership occurs when two or more people come together to conduct business. It's similar to a sole proprietorship in that there is no distinction made between the business and the owners or "partners."
- Independent contractor: An independent contractor is someone who produces work for someone else but is not considered an employee. Independent contractors are often called freelancers because they can work for many different companies at once, or just one. They can decide to stop working for any business at any time, once their contract is finished.
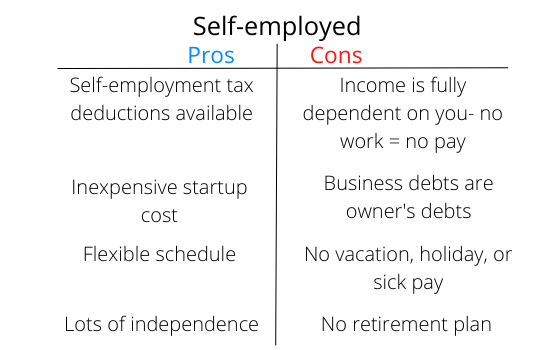
The Pros and Cons of Being Self-Employed
Like any business model, there are positive sides and negative aspects to being self-employed. Here is a quick breakdown.
What Makes Someone a Small Business Owner?
All small business owners are technically self-employed, but not all self-employed people are small business owners.
The main difference? Small business owners can hire others. They often grow beyond solo operations and may manage teams, contractors, or storefronts.
As soon as you hire employees, you’re responsible for:
- Payroll and tax withholding
- Compliance with labor laws
- Workers’ compensation insurance
- Employee benefits (depending on state laws)
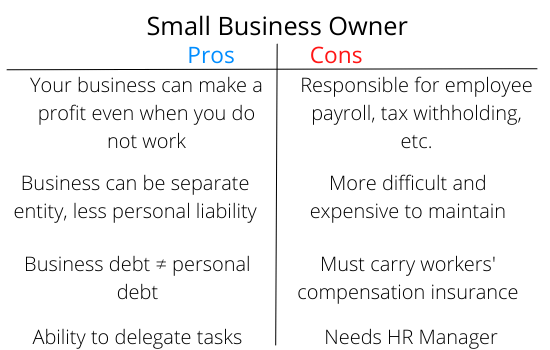
The Pros and Cons of a Small Business Owner
Being a small business owner is a major accomplishment, but it too has positive and negative aspects. Here are some of the pros and cons of being a small business owner.
Tax Differences
Self-Employed?
You’ll pay:
- Self-employment tax (Social Security + Medicare)
- Quarterly estimated taxes
Income passes through to your personal return.
Small Business Owner?
Depends on your business structure:
- Sole proprietors and single-member LLCs → pass-through taxes
- S-Corps or C-Corps → may file separate business returns
Hiring employees also means handling payroll taxes and proper withholding.
Insurance Considerations for Self-Employed and Small Business Owners
Both self-employed individuals and small business owners need protection, especially from liability.
- Self-employed: Consider general liability or professional liability coverage.
- Small business owners: May also be required to carry workers' compensation and commercial property insurance if you have a physical location or employees.
Check your province or state’s requirements to stay compliant.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're a solo consultant or running a growing team, understanding your classification helps you make informed decisions, from taxes to funding to insurance.
Need More Help? Book a 1-on-1 call with a Skip expert.